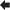 Swipe for more categories
Swipe for more categories 
A Guide to Car Air Conditioning Repair
Warning: Undefined variable $post_id in /var/www/dsw/wp-content/themes/DriveSmart_2024_v1.1/single.php on line 27
April 22, 2019
Warning: Undefined variable $post_id in /var/www/dsw/wp-content/themes/DriveSmart_2024_v1.1/single.php on line 75
A Guide to Car Air Conditioning Repair
Warning: Undefined variable $post_id in /var/www/dsw/wp-content/themes/DriveSmart_2024_v1.1/single.php on line 76
April 22, 2019
Air conditioning is a vital element when it comes to driving in your car with comfort. After all, if we aren’t comfortable, most of us have a difficult time focusing on the task at hand. Driving is a task wherein one should definitely be at maximum focus and, realistically, you should be comfortable in your vehicle. So, when your car is too hot to sit in, it’s time to have a look into car AC repair.
How Does Car Air Conditioning Work?
Your air conditioner doesn’t just cool the vehicle down. It also reduces the humidity (or moisture) in your vehicle. Actually, the air conditioning system does not create cold air. It pulls the heat and moisture out of the air that’s already in your car. An air conditioner’s functions deal with four primary principles:
- Evaporation
- Condensation
- Compression
- Expansion
All this scientific activity going on inside your vehicle is made possible by the five main components to the air conditioning unit. These are:
- The Compressor
- The Condenser
- The Receiver
- The Expansion Valve
- The Evaporator
The AC compressor is the driving force behind the air conditioning system. When the air unit is turned on, the compressor pumps high-pressure refrigerant vapor to the condenser.
The condenser changes the refrigerant vapor into a liquid. The vapor becomes a liquid due to the high pressure that is pushing it forward. This process generates a lot of heat that is removed when air flows through the condenser.
The liquid refrigerant then moves to the receiver. The receiver is a small port where the refrigerant sits to remove any excess moisture. Such moisture in the system would cause major problems like ice blockage and mechanical compromise. Once the pressurized refrigerant reaches the expansion valve, the valve eases the pressure so that the liquid refrigerant can expand to become vapor in the evaporator.
The evaporator takes the cold refrigerant and vaporizes it so that the blower fan can push the cold air throughout the interior of the car. The compressor pulls in the low-pressure vapor to start the cycle over again.
Air Conditioning Not Working in Car
Your air conditioning is not just a luxury. While the air unit does provide comfort, it becomes a necessity on days where hot weather can make the inside of your car rise to heat levels that are dangerous to you and your loved ones. In situations like this, it’s important to ensure that your air conditioner works, and, if it doesn’t, diagnosing the problem will prove quite helpful and time-saving. These are seven of the most common car air conditioning issues:
- Leaking Refrigerant
- Electrical Issue
- Compressor Problem
- Blower Motor
- Faulty Vacuum
- Cables and Connectors
- Condenser is Broken
Leaking Refrigerant
If the refrigerant is leaking in your AC system, it will hinder the unit’s ability to cool the air as it comes through the vents. This can occur anywhere inside the system. For example, the seals, hoses, compressor, or evaporator may be damaged or worn and causing a leak. Since the refrigerant evaporates when exposed to the open air, a visual inspection would do little as far as diagnosing this problem.
If you suspect you may have a leak, listen for a hissing noise from your AC unit or check the condenser for visible damage. Once diagnosed, a problem with refrigerant should be handled by a trained professional because refrigerant is a dangerous chemical.
Electrical Issue
Like any other electrical appliance, your cars AC unit is full of wires and runs on a computer system. So, just like any other electrical appliance, the components and wiring can be worn down for any number of reasons. A trained technician can spot, diagnose, and repair these problems.
Bad Compressor
The compressor moves the refrigerant through the AC system, and also compresses low-pressure refrigerant gas into a high-pressure gas. When it breaks down, the compressor cannot move the refrigerant through the system properly, and thus the air blowing through the vents can’t be cooled down.
The compressor belt or the electrical circuit may be the issue if the compressor isn’t functioning properly. If neither of these components are posing a problem, the compressor itself may need to be replaced. If this is the case, the drive belt should also be replaced if it seems worn out.
Blower Motor
The blower motor is essentially a fan that blows air into your car’s interior. If the blower motor stops working, the cool air that your air conditioner produces will not be distributed into the passenger compartment. This means that either the motor is burned out or the electrical system controlling it is dead.
Faulty Vacuum
The airflow system uses vacuum hoses to keep the flow consistent and direct. If the AC system is losing vacuum somewhere along the way, there must be a leak. If the airflow seems to stop when you’re accelerating, or the flow is only hitting the windshield, this is generally because of a vacuum leak.
Bad Cables
The flaps on the dashboard are directed by a lever or a knob. The cables connect the controlling lever to the flap that directs the air into the passenger compartment. If a cable is broken, the lever and flap will not function.
Condenser is Broken
If the condenser is broken, it should be easy to spot upon visual inspection. The condenser could be punctured from debris coming through the grill at the front end of the car. If this is the case, it simply needs to be replaced. There could also be debris blocking air from coming into the condenser. Clear the condenser of such things like leaves or litter by hand if this is the issue.
Car AC Recharge
If the air coming through your vents is not as cool as it used to be (or if it’s not cool at all), you may need to recharge the air conditioner. This will require cans of refrigerant and can be done at home relatively quickly. However, because of the hazardous nature of the liquid being used, it should be done carefully or left to a professional.
How to Recharge Car AC
The most important thing when recharging your air conditioner is to be sure to use the correct type of refrigerant. Most vehicles manufactured after 1994 use R134a refrigerant. Vehicles made before 1995 used R12 refrigerant which is no longer made. Such a vehicle would require a full AC replacement.
Be sure to use safety glasses and gloves when handling refrigerant. Do not get any of the chemicals on your skin, as it freezes quickly and will be quite painful.
Once you’ve purchased the proper refrigerant, you will need a refrigerant dispenser that has both a pressure gauge and a trigger. Insert the can into the bottom of the dispenser (the dispenser has a pin that will pierce the can when attached).
Step 1: Locate the Refrigerant Fill Port
On the low-pressure side of the AC system, there will be a port with a plastic lid that has an “L” printed on it. Unscrew the cap. If the cap has an “H” you have found the high-pressure port. Do not attempt to use this port.
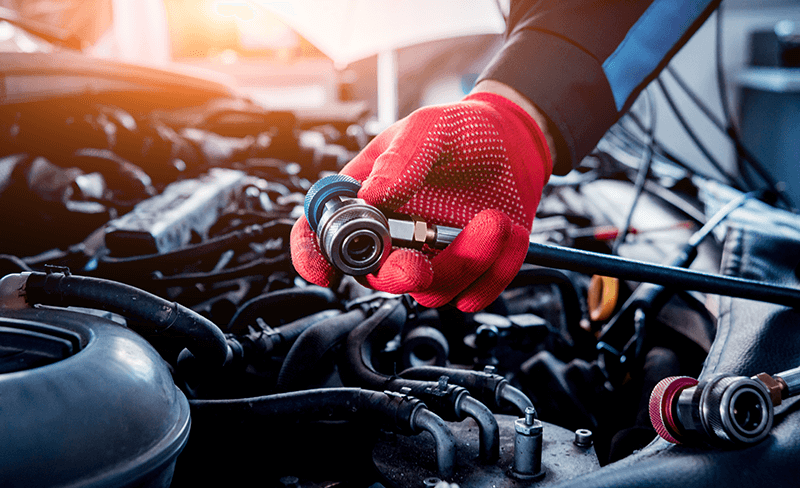
Step 2: Attach the Dispenser and Determine Correct Pressure
Using the gauge on your dispenser, determine the minimum and maximum pressure for the outside air temperature. Squeeze the dispenser trigger for a few seconds to push any air out of the hose. While still squeezing the trigger, push the connector onto the port. Release the trigger once the hose snaps onto the fill port.
Make sure you have your AC unit set to “Max AC.” Wait roughly 30 seconds to ensure your gauge is getting a proper reading. Leave the engine and the AC running until you are finished with the charging process.
Step 3: Charge the AC System
Squeeze the trigger for about ten seconds while slowly tipping and turning the canister. Wait 30 seconds and read the pressure on the gauge. Keep adding refrigerant this way until you reach the appropriate pressure.
Never turn the refrigerant canister upside down.
If you empty the can but require more refrigerant, simply detach the used can from the dispenser and attach the new one. Keep the dispenser hose connected to the fill port while this is done.
FAQ
Does Car Air Conditioning Use Gas?
The use of the air conditioner in your vehicle can increase fuel consumption up to ten percent and negatively affect your gas mileage. Every amenity in your car such as the stereo, AC unit, and heater uses power from the battery. The battery is charged by the fuel in the engine.
To improve fuel efficiency, try driving with open windows when it’s comfortable to do so.
Does Car Air Filter Affect Air Conditioning?
If your air filter is dirty and needs to be replaced, it can clog the air conditioner. Simply cleaning an old air filter is not recommended as it will not properly protect the AC unit.
How Much to Fix AC in Car
Air conditioning repairs can cost anywhere from $100 to $4,000, depending upon the diagnosis. Leaks in the system generally range between $150 and $800. Major repairs that require replacing multiple components like the compressor, condenser, hoses, and valves will likely cost between $1,000 and $4,000.
In order to curtail repair expenses, a vehicle protection plan is a vital asset. Drivesmart’s Powertrain Plus program is a great option for drivers with high mileage vehicles who want to avoid expensive repairs on things like air conditioning. Newer vehicles with lower mileage can benefit even further with Drivesmart’s Elite plan. Whatever car or truck you’re driving, Drivesmart has a protection plan tailored to keep the cash in your pocket when things go wrong.
"> /var/www/dsw/wp-content/themes/DriveSmart_2024_v1.1/single.php on line 177
">
"> /var/www/dsw/wp-content/themes/DriveSmart_2024_v1.1/includes/quote-modal.php on line 8
">


