 Swipe for more categories
Swipe for more categories 
How Does a Car Radiator Work?: Radiator Repair and Function
Warning: Undefined variable $post_id in /var/www/dsw/wp-content/themes/DriveSmart_2024_v1.1/single.php on line 27
July 3, 2019
Warning: Undefined variable $post_id in /var/www/dsw/wp-content/themes/DriveSmart_2024_v1.1/single.php on line 75
How Does a Car Radiator Work?: Radiator Repair and Function
Warning: Undefined variable $post_id in /var/www/dsw/wp-content/themes/DriveSmart_2024_v1.1/single.php on line 76
July 3, 2019
When we drive our cars, most of us aren’t really thinking about the complex mechanics of its inner workings. If it starts, accelerates, and stops when we want it to, we’re pretty much satisfied. However, commonly overlooked components like the Radiator are paramount to the vehicle’s smooth performance and longevity. A car radiator keeps you from landing on the side of the highway with an undrivable vehicle. In order to avoid this scenario, it’s good to know how a car radiator works as well as the fundamentals of car radiator repair.
What is a Radiator in a car: What Does a Radiator Do
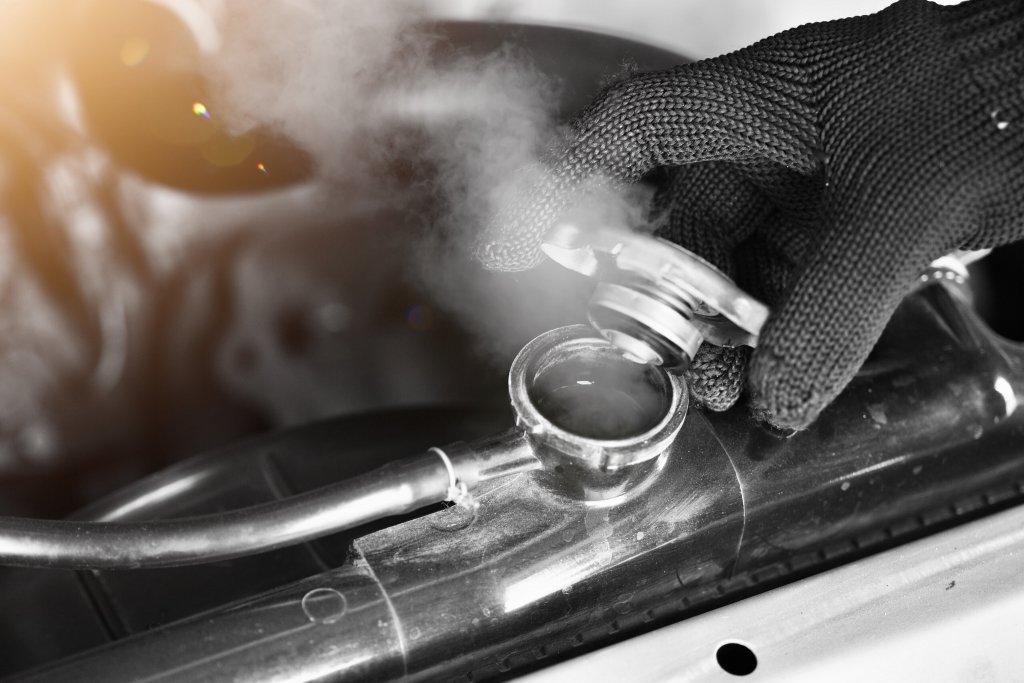

A car radiator is a heat exchanger that transfers the heat of the fluid flowing through it to the air that blows through it from the front of the vehicle guided by the radiator fan. Just as a radiator in a building releases the heat collected within it, a car radiator collects and releases the heat produced by the engine to prevent engine overheating.
How a Car Radiator Works
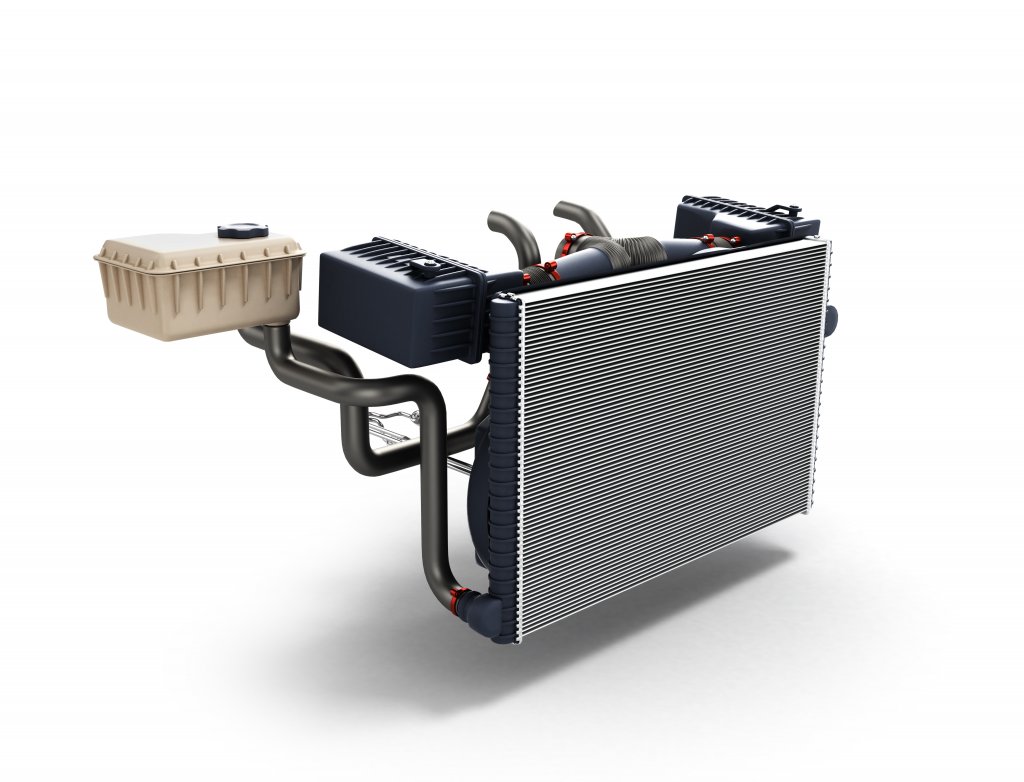

As the engine in a car burns fuel, it produces a tremendous amount of heat. If this heat is not displaced properly, it can destroy car engine parts and thus, the engine itself. The cooling system works in a cycle in which the radiator cools the heated antifreeze coolant before it returns to the engine. These are the steps involved when an engine is cooled by a radiator:
- As the engine does its work, it heats up the coolant fluid that is designed to absorb the excess heat the engine creates.
- Once the antifreeze begins nearing its boiling point, it is released through a radiator hose to the radiator.
- The antifreeze passes through tubes in the radiator as the heat it has absorbed is released into the atmosphere. This process is assisted by the radiator fan.
- Because the fluid expands as it heats, it creates pressure. If the cooling system reaches a certain pressure point, the radiator cap acts as a release valve that opens and releases steam.
- Any excess coolant is then allowed to escape into the radiator overflow tank attached to the side of the radiator.
- Once the antifreeze is sufficiently cooled it is sent through another hose back to the engine.
Bad Radiator Symptoms
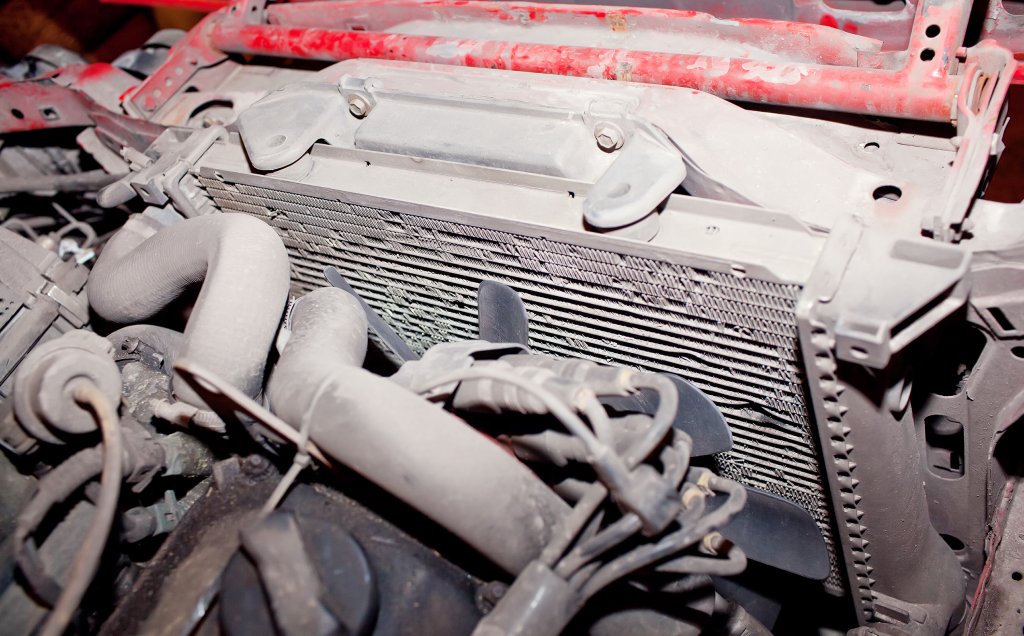

If the radiator is not operating correctly in a vehicle, it can become a very serious problem. Knowing the signs of car radiator problems can prevent expensive breakdown repairs as well as unsafe driving situations. Some tell-tale bad radiator symptoms are:
- Car Overheating: If the vehicle is continuously overheating, this is a very common sign that the radiator is failing. The radiator’s only function is to cool the engine and transmission. If the radiator doesn’t perform its duties, the heat created by the engine cannot be displaced. This is one of the main reasons for car overheating. However, there are several other simpler car overheating causes such as low coolant levels in the system.
- Coolant Leak: A car leaking antifreeze is not necessarily coming from the radiator, but it is indicative of a serious problem in the cooling system. An antifreeze leak will be easy to spot. The coolant will be a bright yellow, green, or red fluid and a leak will be apparent as the coolant will pool beneath the vehicle when it is parked. Antifreeze can leak from anywhere in the system; including the engine block, water pump, radiator, and hoses. A car leaking coolant should be dealt with quickly, before it leads to more complicated and serious problems.
- Sludge Buildup in Radiator: If the coolant in the vehicle has a rusty or oily color, it means there’s a problem with the radiator. The antifreeze changes color when sludge builds up in the radiator. This occurs when the radiator is rusting or corrosion has caused transmission oil to mix with the coolant. If this is the issue, radiator replacement is needed to curtail extensive engine and transmission issues.
- White Smoke from Engine: White smoke coming from under the hood or the tailpipe is a sign that the engine coolant is boiling and the pressure in the system is not being released properly. This could be due to a problem with the radiator hoses or the radiator cap. If the radiator cap is not functioning properly, the antifreeze is heating and expanding, but the pressure is not being released. Steam is being forced from the engine while the antifreeze burns and mixes to create white smoke.
- Low Coolant: When a vehicle needs to have the coolant replenished frequently, it is most likely due to a leak. If the antifreeze level seems constantly low or the Low Coolant light comes on regularly, one of the components in the cooling system, such as the radiator, is leaking fluid. Vehicles with antifreeze leaks need to be repaired immediately before irreparable damage to the engine and transmission occurs.
Auto Radiator Repair Services
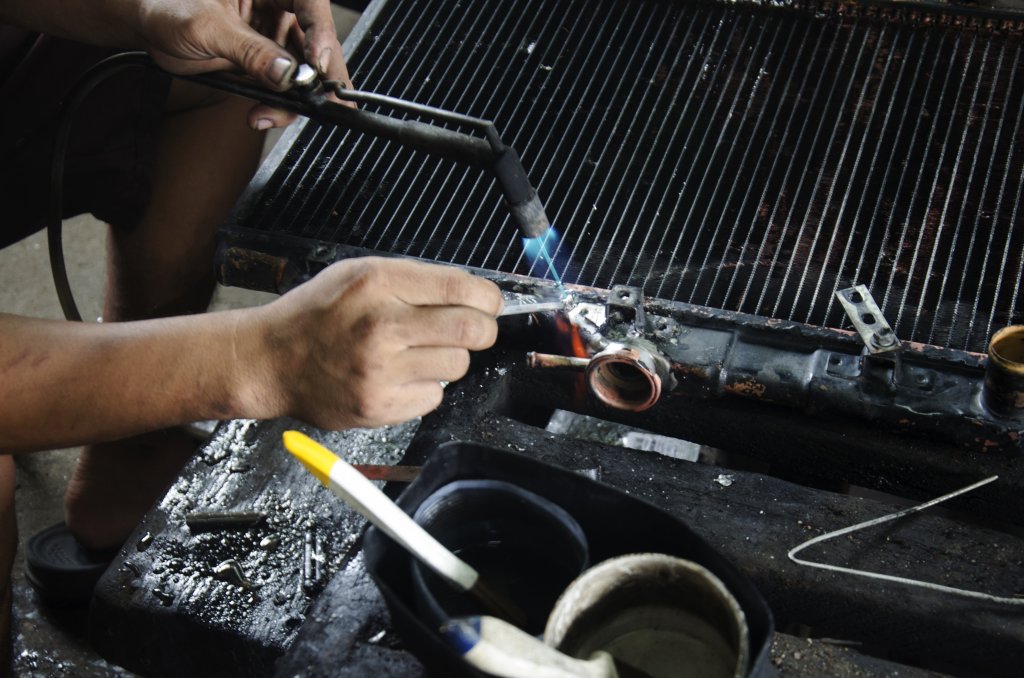

A radiator must work properly at all times. The cooling system works in a constant cycle and the radiator is the key point along the route for the coolant fluid to expel heat. It’s important to maintain the function of the radiator, as well as the cooling system at large, to ensure that the vehicle doesn’t begin to overheat on the road. These are some common causes for radiator problems:
- Radiator Fan: The Thermostatically controlled fan behind the radiator, as well as the air naturally flowing through the front of the car, cools the antifreeze mixture as it enters the radiator. If the radiator fan isn’t working properly, the car may overheat when parked or idle. In this case, the fan or it’s motor need to be replaced.
- Blocked Radiator: Debris such as dirt, leaves, and litter can become attached to the radiator. This debris obstructs the flow of air through the radiator and keeps it from properly cooling the antifreeze. Clearing the radiator off by hand or with a brush should be sufficient in eliminating this problem.
- Rust and Corrosion: Although a modern aluminum radiator is built to be rust-resistant, corrosion is still possible. If the antifreeze is not properly mixed with water (or the antifreeze is old) it can begin to cause corrosion within the radiator and result in leakage. Some radiators have plastic parts that can crack over time as well. In this case, a licensed mechanic will know how to fix a radiator leak. If the leak cannot be mended, the radiator must be replaced.
How to Replace a Radiator
If you are someone who considers yourself to be mechanically inclined, you can replace a bad radiator on your own. Remember that all manufacturers build vehicles differently and this means that removal and installation of a radiator may differ slightly in procedure from car to car. With this in mind, knowing how to change a radiator can save you a lot of cash on repair bills and labor costs. A Radiator can be removed and replaced by following these simple steps:
- Step 1: Check the radiator and hoses to ensure that the coolant inside is not hot. A hot radiator should never be opened, as hot coolant can burn you severely.
- Step 2: Before the radiator can be removed, the coolant needs to be drained. Some radiators will have a drain on the bottom that can be opened with socket wrench. If the radiator has no drain, simply remove the clamp on the lower radiator hose and pull the hose end free. Be sure to have a drain pan ready to collect the coolant as it drains. Opening the radiator cap while draining will allow the fluid to drain quickly and with little splash.
- Step 3: Make sure any additional lines that run to the radiator are disconnected. Some radiators have a transmission cooler built into them and these lines will also need to be disconnected before the radiator can be removed.
- Step 4: Begin to remove the upper and lower radiator hoses. Loosen the radiator hose clamps using pliers or a screwdriver. Pinching clamps will require pliers; worm-gear clamps will need a screwdriver. Remove the hoses by twisting and pulling them away from the connection point.
- Step 5: Disconnect the electric radiator fan from its connector. Using a socket wrench with the appropriate socket size, remove the cooling fan’s mounting bolts. You can then remove the radiator fan.
- Step 6: Remove the radiator’s mounting bolts with a socket wrench. You may then lift the radiator out of the engine bay. Mount the new radiator into position and secure it with the mounting bolts.
- Step 7: Reverse the steps for removal of the radiator. While installing the new radiator, if there are any caps over the fluid connection points, keep the caps on until the connection is being made. Removing them early will permit contaminants to enter the radiator. Once the radiator is installed, fill it with the proper mixture of antifreeze and water.
- Step 8: Turn the engine on in order to circulate the antifreeze through the cooling system. Turn the heater controls all the way up in the passenger compartment and let it run. This will allow coolant to flow into the heater core and push any air from the cooling system.
Radiator Replacement Cost: How Much is a Radiator
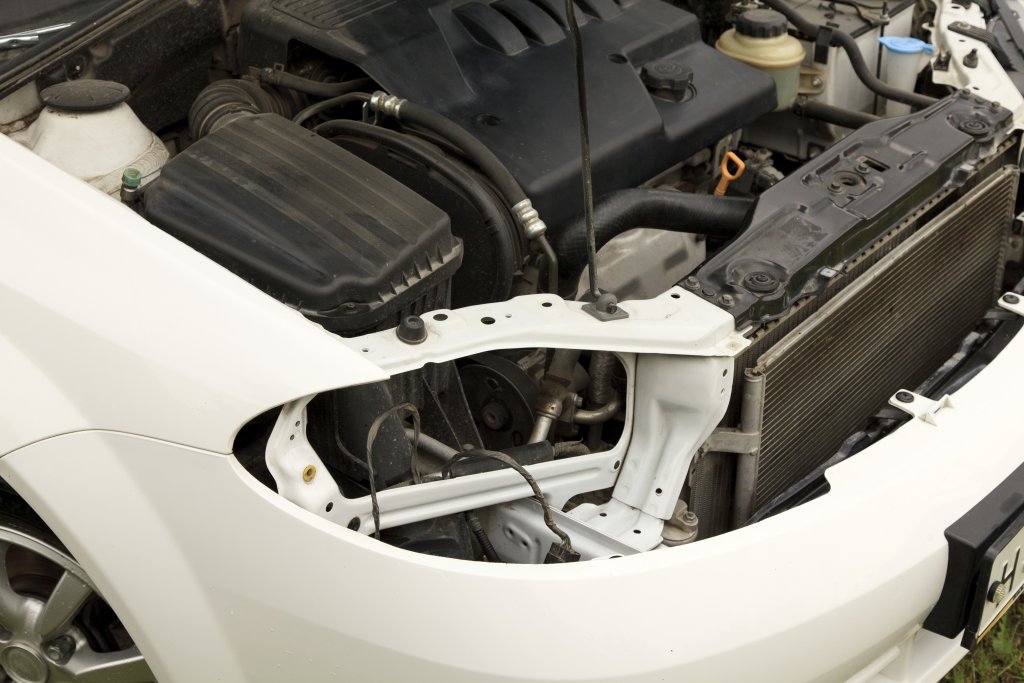

If you need to replace your radiator, it tends to be an expensive endeavor. Radiator cost is estimated to range between $150 and $700. If your going to have the radiator replaced by a professional, with parts and labor costs applied, the price ranges between $300 and $1200.
Having a reliable service contract on your vehicle is the perfect way to steer clear of such high cost repairs. Getting protection on your vehicle before it overheats is important. Once a car or truck overheats, it immediately begins to cause damage to the vehicle. Without having a protection plan on your vehicle beforehand, these heavy repair bills can be a major burden on your bank account.
Drivesmart’s Advantage plan covers all repairs on radiators, radiator fans, water pumps, and more. If your vehicle has less than 175,000 miles, the Advantage plan may be the best protection plan for your car.
"> /var/www/dsw/wp-content/themes/DriveSmart_2024_v1.1/single.php on line 177
">
"> /var/www/dsw/wp-content/themes/DriveSmart_2024_v1.1/includes/quote-modal.php on line 8
">


